Medical history form

The Medical history form helps you collect medical history of a patient for the purpose of onboarding a new patient. It helps you gather a detailed overview of the patient's current and past health. It also helps you decide whether your doctor's office is equipped to properly treat the conditions that the patient has reported.










Medical history form FAQs
The purpose of a medical history form is multifaceted, serving both healthcare providers and patients in various important ways. Here are the key uses and benefits of a medical history form:
1. Comprehensive Patient Evaluation
- Gathering Background Information: Provides a detailed overview of the patient's past and present health, including chronic conditions, surgeries, allergies, and medications.
- Identifying Risk Factors: Helps identify potential risk factors for diseases and conditions based on the patient’s personal and family medical history.
2. Facilitating Diagnosis
- Symptom Correlation: Assists in correlating current symptoms with past medical issues or treatments, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
- Pattern Recognition: Helps healthcare providers recognize patterns or recurring issues that may indicate a specific diagnosis.
3. Treatment Planning
- Personalized Care: Enables the development of tailored treatment plans that consider the patient’s unique medical background.
- Medication Management: Assists in managing medications by considering previous and current prescriptions, preventing adverse drug interactions.
4. Continuity of Care
- Reference for Multiple Providers: Serves as a reference for different healthcare providers involved in the patient's care, ensuring consistency and continuity.
- Tracking Progress: Allows for tracking the progress of treatments and conditions over time, facilitating ongoing care and adjustments as needed.
5. Preventive Care
- Screening and Vaccinations: Guides recommendations for preventive measures such as screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle changes.
- Early Detection: Promotes early detection of potential health issues based on family history and known risk factors.
6. Legal and Administrative Uses
- Documentation: Provides official documentation of the patient’s health history, which can be important for legal and insurance purposes.
- Compliance: Ensures compliance with healthcare regulations and standards by maintaining thorough and accurate medical records.
7. Enhancing Communication
- Patient-Provider Communication: Improves communication between patients and healthcare providers by providing a clear and comprehensive health overview.
- Patient Engagement: Engages patients in their own care by encouraging them to reflect on and discuss their health history.
8. Research and Public Health
- Data Collection: Contributes to data collection for medical research and public health studies, aiding in the understanding of health trends and outcomes.
Key Components of a Medical History Form
- Personal Information: Name, age, gender, contact information.
- Medical History: Past and current medical conditions, surgeries, hospitalizations, allergies, and immunizations.
- Medication List: Current and past medications, including dosages and duration of use.
- Family Medical History: Health conditions of immediate family members, such as parents and siblings.
- Lifestyle Information: Habits such as smoking, alcohol use, diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors.
- Symptoms and Complaints: Description of current symptoms and concerns.
- Review of Systems: Systematic review of different body systems to identify any additional symptoms or issues.
By comprehensively documenting these aspects, a medical history form ensures that healthcare providers have the necessary information to deliver high-quality, personalized care.
A comprehensive medical history form is essential for providing quality healthcare. It should request detailed and pertinent information from patients, including but not limited to the following:
Personal Information
- Full Name
- Date of Birth
- Gender
- Contact Information (phone number, email, address)
- Emergency Contact details
Health Insurance Information
- Insurance Provider
- Policy Number
- Group Number
- Policyholder Name and Relationship to Patient
Primary Care Physician Details
- Name
- Contact Information
Current Medications and Supplements
- Prescription Medications
- Over-the-Counter Medications
- Herbal Supplements
- Vitamins
Allergies and Sensitivities
- Medication Allergies
- Food Allergies
- Environmental or Seasonal Allergies
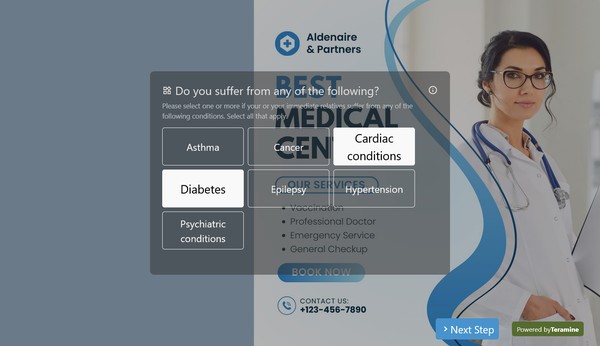
Medical Conditions and History
- Chronic Conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
- Past Surgeries and Hospitalizations
- Significant Illnesses (e.g., cancer, heart disease)
- Mental Health Conditions
Family Medical History
- Hereditary Conditions (e.g., genetic disorders)
- Major Health Issues in Immediate Family Members (e.g., parents, siblings)
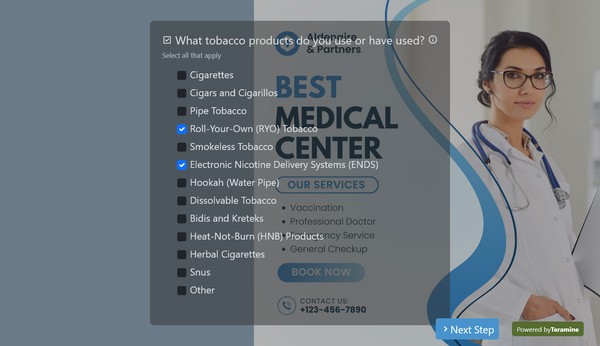
Lifestyle and Social History
- Smoking, Alcohol, and Drug Use
- Exercise Habits
- Diet and Nutrition
- Occupational Exposures or Hazards
Reproductive History (if applicable)
- Number of Pregnancies and Outcomes
- Menstrual History
- Contraception Use
Vaccination and Immunization Records
Review of Systems
- Cardiovascular
- Respiratory
- Gastrointestinal
- Genitourinary
- Musculoskeletal
- Neurological
- Dermatological
- Endocrine
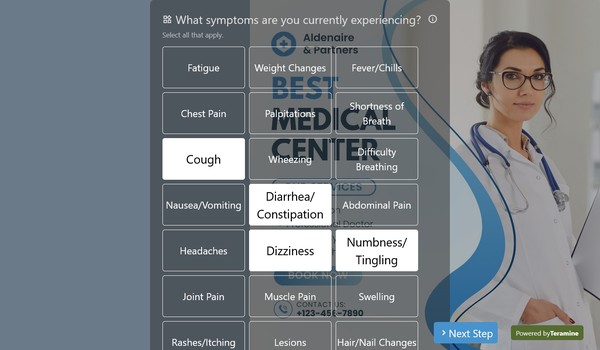
Symptom Check
- Current Symptoms and Concerns
- Pain Scale and Description
- Duration and Frequency of Symptoms
Advanced Directives and Consent Forms
- Living Will
- Durable Power of Attorney for Healthcare
Each section should be designed to capture accurate and complete responses to ensure the healthcare provider can offer the most effective and personalized treatment. Patients should be reassured about the confidentiality and security of their information to encourage full disclosure.